nserman@fsb.hr Transfer Function Concept Digest
7. BLOCKS ALGEBRA
All the interactions within any SISO blocks system regardless of its complexity can be described by a combination of the elementary interactions presented in fig. 7.1.
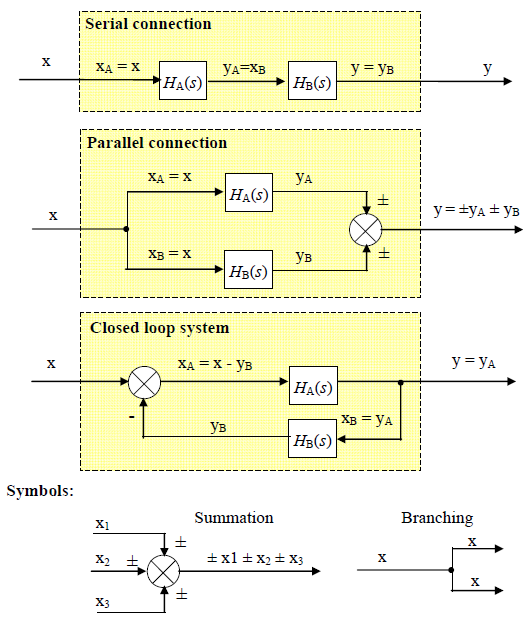
Fig. 7.1 Elementary interactions between blocks
In the time domain relationship between system input x(t) and output y(t) is described by a differential equation. When mapped into the frequency domain it turns into a simple algebraic relation (4.5).
By applying elementary blocks algebra from Fig 7.1 the following relations between transfer function components and respective system transfer functions take place:
For blocks in series:
![]()
For blocks in parallel:
![]()
For blocks in negative feedback closed loop:
![]()
The numerator in (7.3) depends on the system’s output. The denominator is always a sum of 1 plus a product of all the transfer functions within the closed loop.
The product in the denominator can be understood as a serial connection of the block HA(s) and HB(s). We call it open-loop transfer function W(s):
![]()



